Chile is rising as a worldwide leader in the green hydrogen sector, thanks to its plentiful solar and wind energy resources. Electrolyzers are essential for advancing green hydrogen in the energy transition. Electrolyzers use renewable electricity to separate water into hydrogen and oxygen. Chile will have its initial electrolyzer manufacturing plants after Corfo provided US $25.6 million in funding. The initiative supported by Corfo will enable the establishment of facilities in Chile with an investment surpassing $50 million. Green hydrogen plays a vital role in Chile’s renewable energy industry by substituting coal in steel manufacturing, natural gas in ammonia and fertilizer production, and diesel in mining activities. Electrolyzers rely on stable and high-quality electrical current to separate water via electrolysis. C-span clamps are essential for securing and stabilizing pipelines, cables, or various other components.
A well-designed C-span clamp ensures the safe and efficient operation of the infrastructure. The use of C-span clamps in electrolyzer factories ensures reliability, scalability, and safety. The clamp function in the construction and operation of electrolyzer factories. This contributes to the efficiency and safety of green hydrogen production in Chile. Chile is scaling up its green hydrogen production, which needs the reliability of electrolyzer components. High-quality C-span clamps also anchor and stabilize frameworks and ensure the integrity of the factory’s infrastructure. This is crucial, as Chile aims to produce some of the cheapest green hydrogen to remain competitive in international markets.
Main initiatives and their effects in Chile’s renewable energy industry
Chile is progressing its green hydrogen industry by implementing various important electrolyzer initiatives. The initiatives are anticipated to influence Chile’s energy landscape in many ways. Important initiatives encompass AES Chile’s Inna project, a large renewable hydrogen and ammonia production facility designed to capitalize on the region’s renewable energy possibilities. The green hydrogen facility of Engie and Walmart Chile demonstrates the real-world use of green hydrogen in logistics and supply chain activities. These initiatives affect Chile’s energy industry by diversifying energy sources, pursuing decarbonization, and promoting economic development.
The role of C-span clamps in electrolyzer factories
C-span clamps are crucial in green hydrogen production in developing electrolyzer factories. The clamps ensure the stability, safety, and efficiency of electrical and piping systems. C-span clamps play a crucial role in the electrical and mechanical infrastructure stability. They support high-power connections, secure hydrogen pipelines, resist corrosion, and enhance seismic resilience. This is crucial in ensuring safe and efficient electrolyzer factory operations. Common types of electrolyzers used in electrolyzer factories include compression splices, mechanical splices, and heat-shrink and cold-shrink splices. Their key roles include:
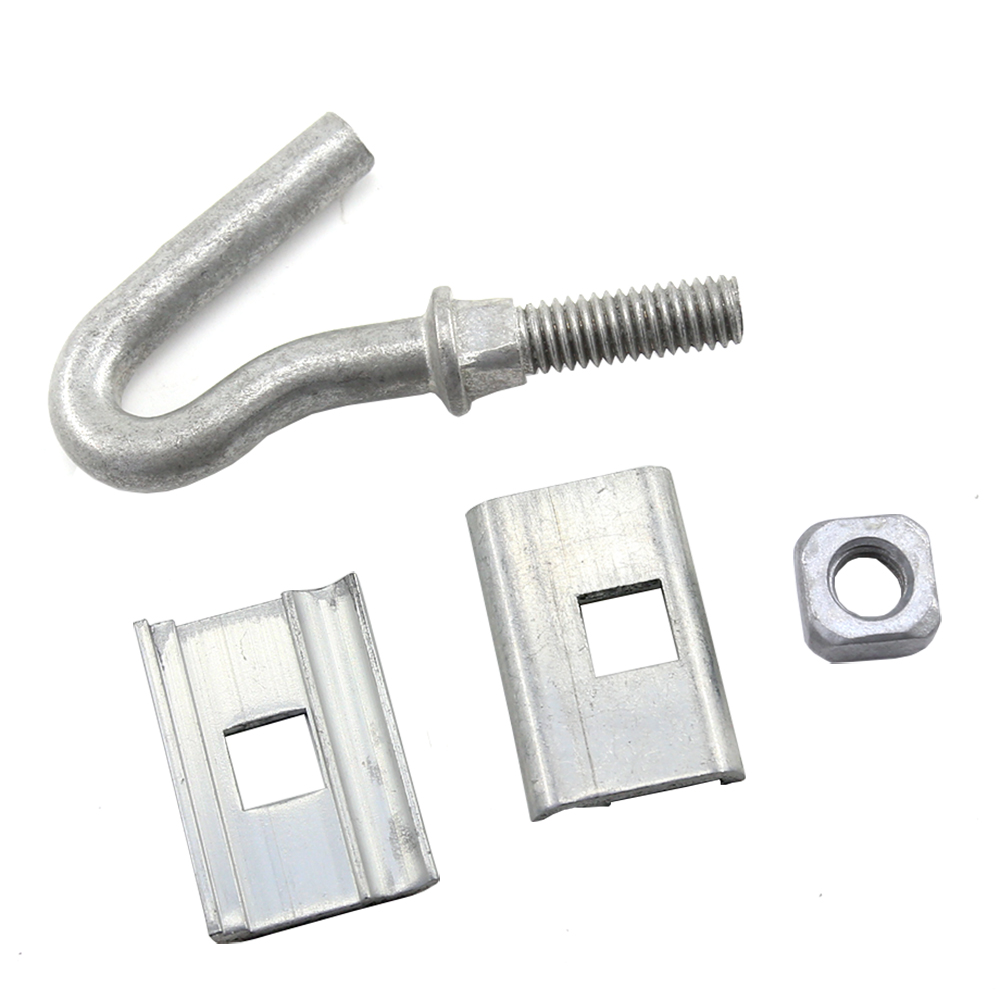

- Electrical conductor support and insulation—electrolyzer factories need high-current DC power to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. C-span clamps help secure and support electrical conductors used in power distribution. This prevents sagging and reduces the risks of electrical faults.
- Mechanical stability in hydrogen piping systems—green hydrogen production involves high-pressure gas pipelines. C-span clamps provide secure fastening for pipes and tubing. This reduces vibration and mechanical stress. C-span clamps prevent pipe movement due to thermal expansion, pressure fluctuations, or seismic activity.
- Resistance to harsh environments – C-span clamps are made from stainless steel or polymer-coating materials. These are able to resist corrosion, oxidation, and chemical degradation to ensure long-term durability.
- Ease of maintenance and installation – the clamps are lightweight, modular, and easy to install. This reduces downtime in factory construction. C-span clamps allow for quick adjustments or replacements that make maintenance more efficient.
Technologies aiding the advancement of electrolyzer manufacturing in Chile
Significant progress has been made that facilitates the establishment of electrolyzer plants in Chile. Anticipated to start in 2026, electrode technology enhances advancements in energy, automation, and infrastructure. The performance of the electrolyzer plants will rely on these technologies to improve efficiency, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Here are the main technologies.

- Sophisticated electrolyzer technologies—these encompass proton exchange membranes, alkaline electrolyzers, and solid oxide electrolyzers.
- The incorporation of renewable energy encompasses smart grid technology, AI-powered energy management, and combined solar-wind energy systems. Conductor splices are essential for combining these technologies within electrolyzer production facilities and the power grid.
- Digital and automation technologies—industrial IoT and predictive maintenance—decrease downtime, enhance equipment longevity, and boost operational efficiency. Moreover, automation boosts production rates, lowers expenses, and improves quality assurance in electrolyzer manufacturing facilities.
- Innovations in hydrogen storage and distribution—progress in hydrogen storage enables safe and effective transportation over long distances. Additionally, green hydrogen can be transformed into ammonia and e-fuels for easier storage and transportation.