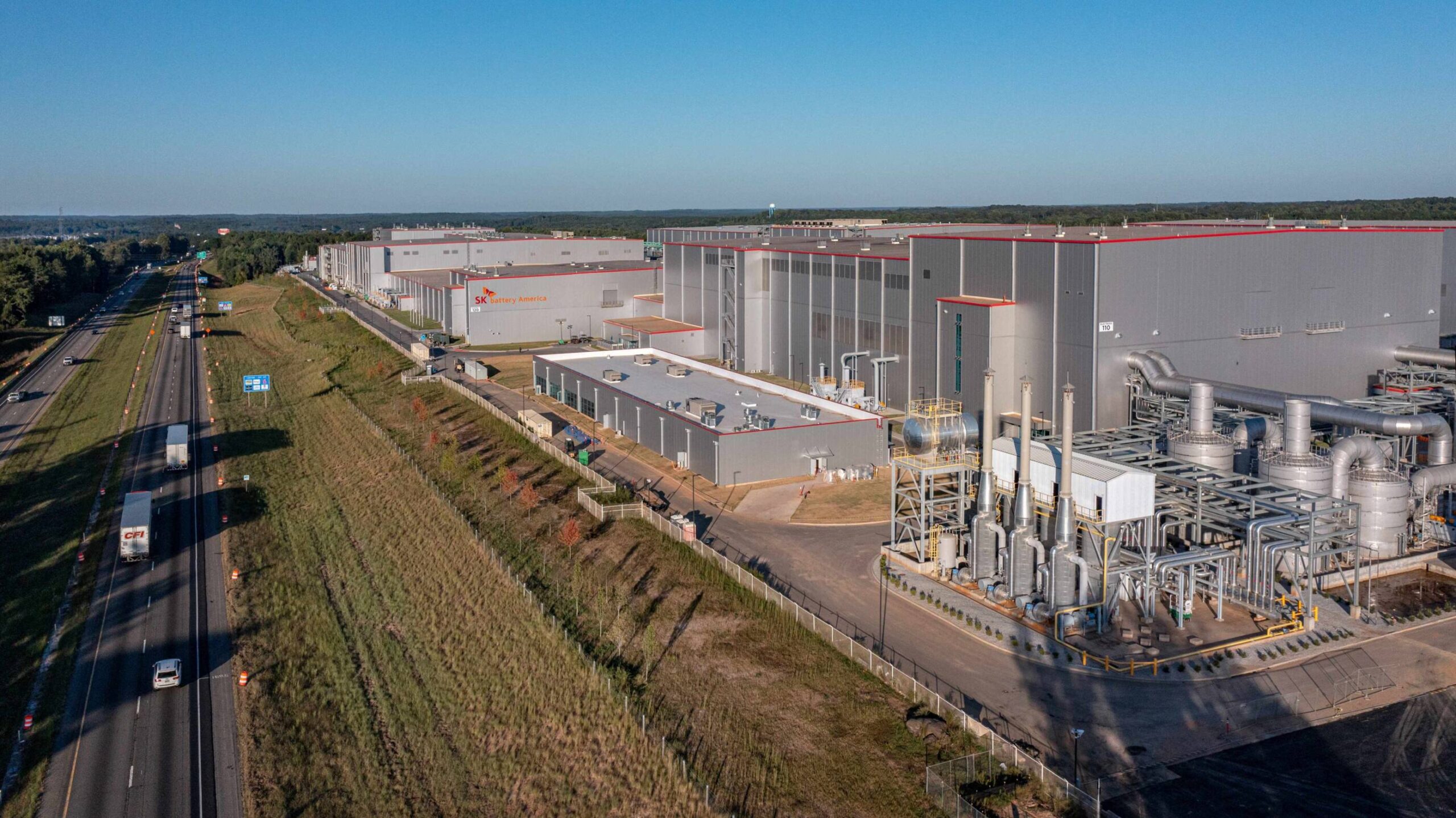
Chile aspires to establish itself as a worldwide frontrunner in green hydrogen production by utilizing its plentiful renewable energy assets, encouraging government regulations, and helpful geographic placements. Green hydrogen is generated by the electrolysis of water powered by renewable energy sources. Chile possesses abundant natural resources that are perfect for generating solar and wind energy, particularly in regions such as the Atacama Desert and Magallanes. It also seeks to establish Chile as one of the leading three exporters of green hydrogen by 2040. It has also pledged to meet carbon neutrality by 2050, with green hydrogen being vital to decarbonization initiatives. Ongoing investment in innovation, infrastructure, and collaboration can assist Chile in reaching its ambitious targets for green hydrogen. Projects for green hydrogen production need strong power transmission and distribution networks backed by guy clamps.
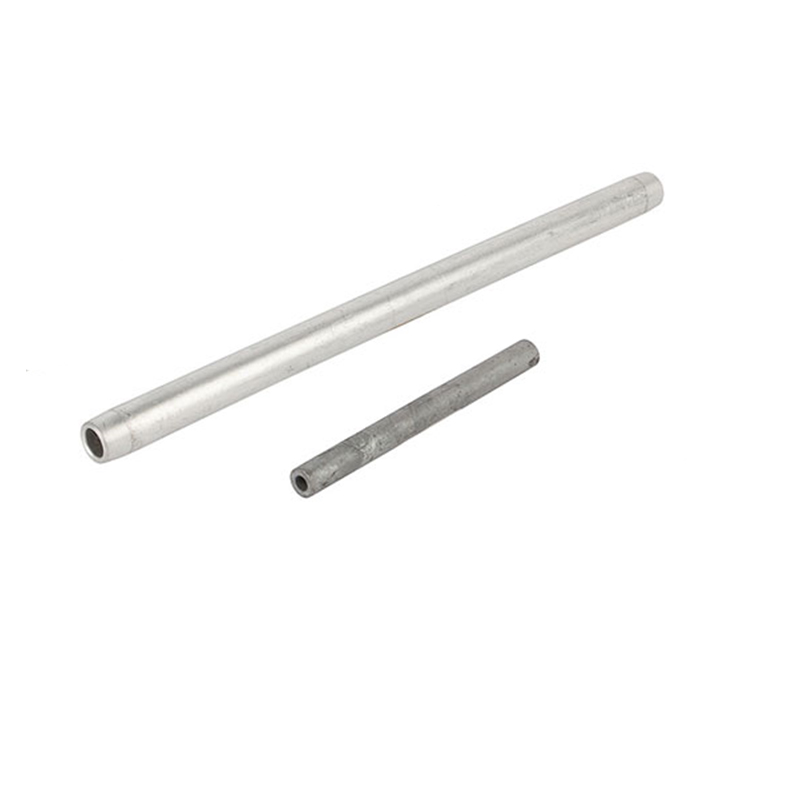
A guy clamp is crucial hardware used in securing and tensoning guy wires. Guy wires stabilize utility poles, transmission structures, and industrial infrastructure. The use of guy clamps ensures the stability of power and support structures in Chile’s green hydrogen sector. They also ensure stable and resilient power transmission, industrial structures, and hydrogen infrastructure. Guy clamps secure guy wires that stabilize poles and towers to prevent swaying or collapse under high wind conditions. The electrolyzers for green hydrogen also use guy clamps to support cooling towers, hydrogen storage tanks, and compressor stations.
Functions of guy clamps in green hydrogen production in Chile
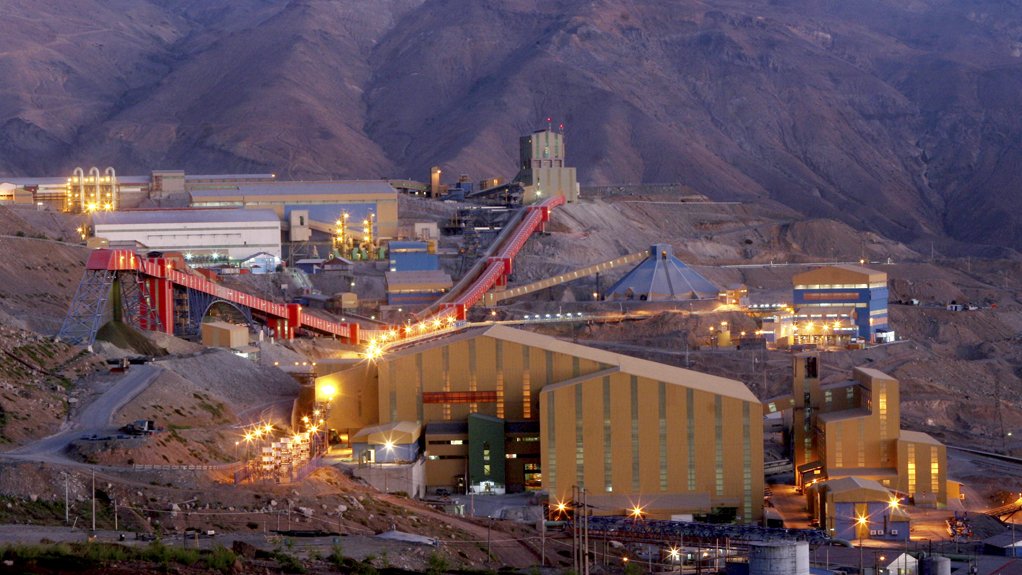
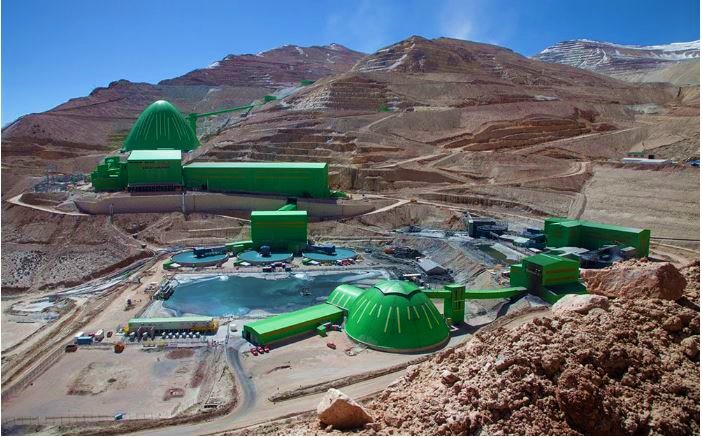
Guy clamps are crucial components used in the construction and stabilization of structures. They provide support to utility poles, towers, and other installations to withstand external forces. Guy clamps are crucial for supporting the infrastructure necessary for green hydrogen projects. They play a crucial role in supporting renewable energy generation, electricity transmission, and hydrogen distribution networks. Additionally, the clamps stabilize power lines for electrolyzers, infrastructure for hydrogen transport, grid expansion, and ensure safety and reliability.
Innovations in technology employed for hydrogen generation in Chile
Several technological innovations are applied to enhance green hydrogen production in Chile. They enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve scalability. The application of cutting-edge technologies aids in tackling significant challenges and creating new possibilities. Chile has the potential to strengthen its role as a worldwide leader in green hydrogen production, aiding the global energy transition. Here are the technological innovations supporting green hydrogen production in Chile.

- Innovative electrolyzer technologies—significant advancements include high-efficiency electrolyzers designed to manage the fluctuating output of renewable energy sources.
- The integration of renewable energy—producing green hydrogen is incorporating innovations in energy integration to make the most of solar and wind resources. Other advancements include hybrid renewable systems, direct coupling, and intelligent grid technologies.
- Energy storage systems—capturing surplus renewable energy for use when generation is low is essential for producing green hydrogen. The advancements encompass battery storage, hydrogen storage, and ammonia used as a storage medium.
- Carbon capture and utilization (CCU) – CCU technologies enhance hydrogen production by lowering emissions in associated sectors. Carbon capture and methanation represent the primary advancements in green hydrogen.
Main obstacles to green hydrogen production in Chile
Chile’s energy industry needs to tackle many challenges to fully seize the potential for producing green hydrogen. The difficulties may stem from technical, economic, logistical, and regulatory areas. Addressing these obstacles via innovation, funding, and teamwork can assist Chile in realizing the complete potential of its green hydrogen sector. Outlined below are the main obstacles confronting green hydrogen production within Chile’s energy industry.

- Significant upfront capital expenses—particular issues involve the costs of electrolyzers, the infrastructure for renewable energy, and the facilities for storage and transportation.
- Infrastructure development – Chile does not have the required infrastructure to ease extensive green hydrogen production, storage, and export. Obstacles consist of hydrogen pipelines, export port facilities, and renewable energy sources in distant areas.
- Technological advancement—this encompasses electrolyzer efficiency to cut energy losses, resilience against environmental factors, and hydrogen storage capabilities.
- Market demand – the worldwide green hydrogen market is still emerging, and the demand for green hydrogen remains unpredictable. Challenges stem from the absence of an offtake agreement, rivalry with gray hydrogen, and the progression of the export market.