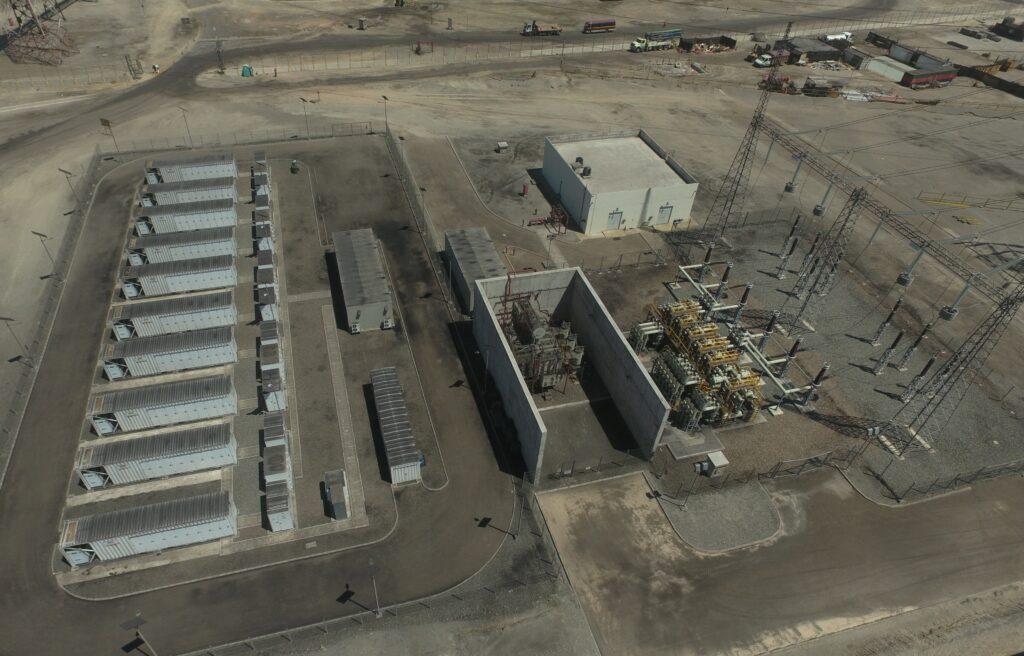
Peru seeks to address the increasing need for steady and dependable electricity by establishing lithium battery installations. The country has the ability to include lithium battery production and recycling facilities into its energy infrastructure. It promotes renewable energy expansion, electric mobility, and industrial development. Peru continues to deploy green energy technologies such as solar, wind, and hydropower to phase out the use of fossil fuels. Lithium batteries can help to stabilize the grid by storing extra renewable energy, reducing the need for diesel, and supporting microgrids. The 500 kg/h recycling system might recover lithium, cobalt, and nickel for reuse while reducing e-waste pollution from imported devices. The Peruvian energy sector can profit from lithium battery installations. It could enable renewable energy storage, EV adoption, and sustainable mining and industrial electrification. Using downlead clamps in the infrastructure ensures efficient energy transfer, operational safety, and system reliability.
Downlead clamps are important electrical and structural components in lithium battery installations. They are critical for power distribution, safety, and equipment communication. High-performance downlead clamps are used in battery cell assembly processes, energy storage systems for grid stabilization, and battery recycling equipment. Lithium battery operations need high-current connections for electrode coating equipment, battery construction and testing systems, and industrial shredders. Downlead clamps cut voltage drop, which improves energy efficiency. Downlead clamps in battery facilities improve power distribution, safety, and long-term reliability. This is critical for the efficient operation of Peru’s lithium battery installations.
Purpose of downlead clamps in lithium battery plant construction in Peru.
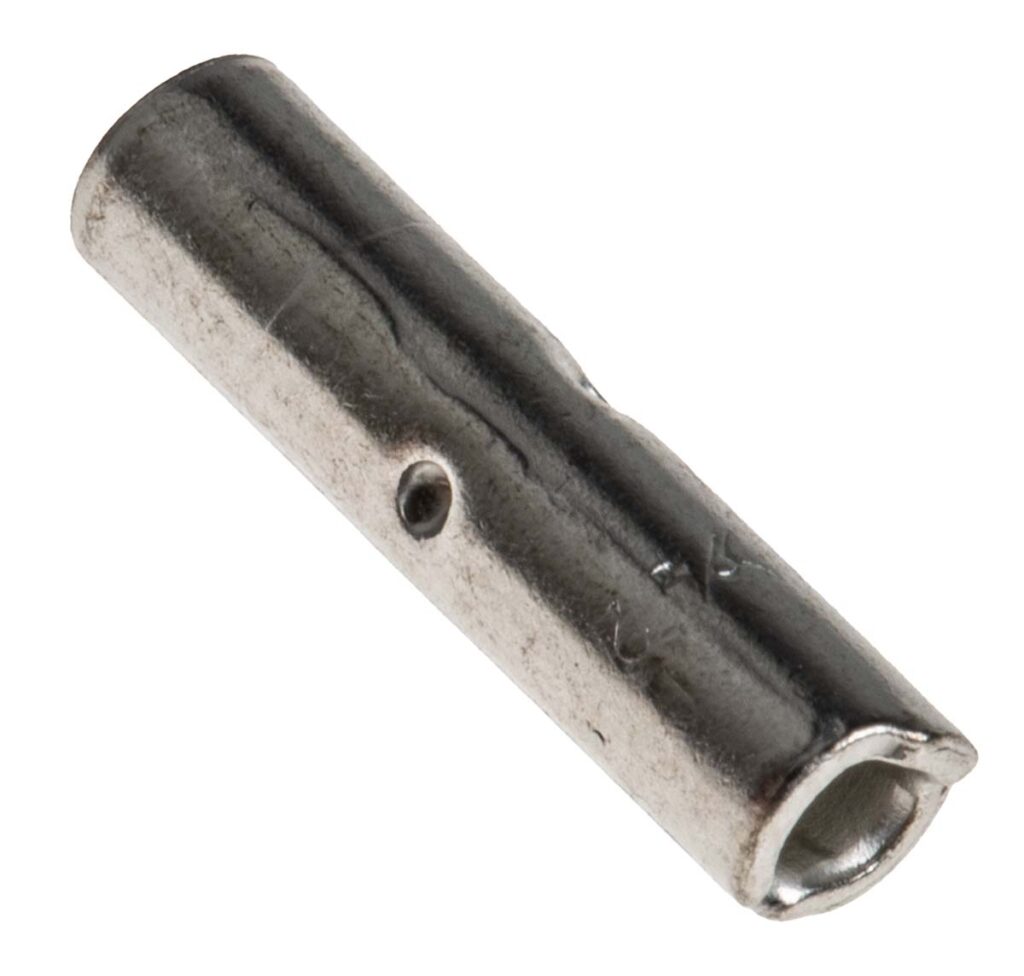
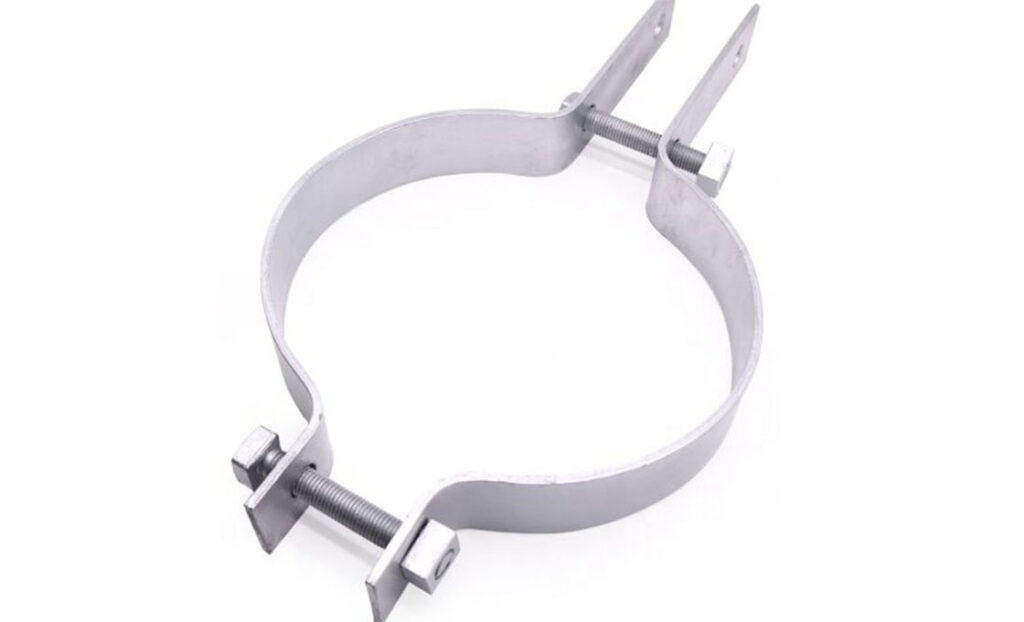
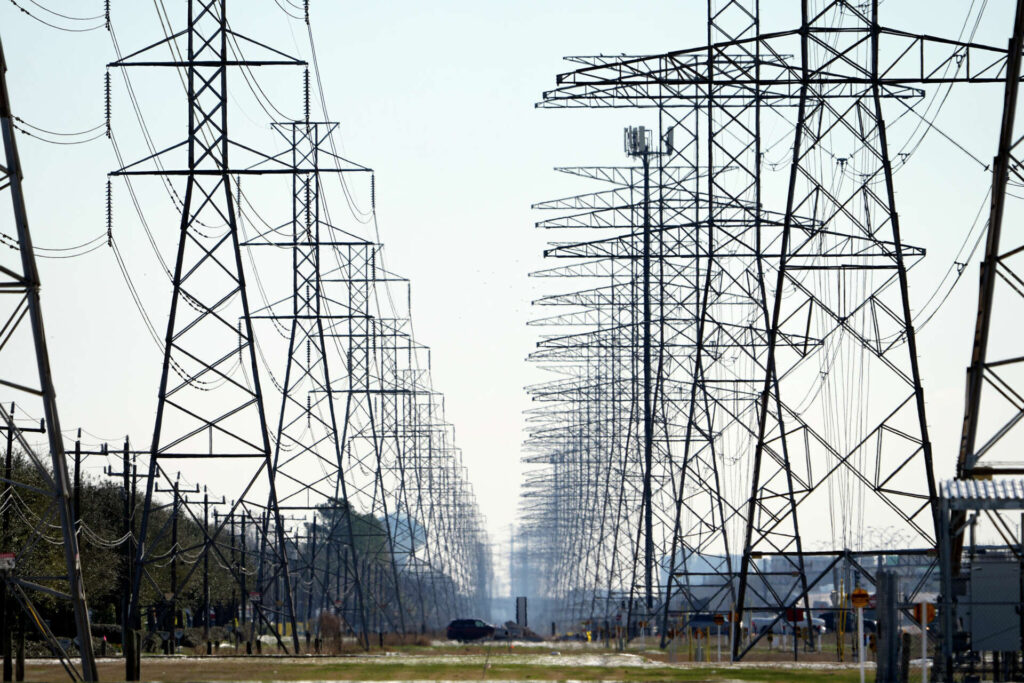
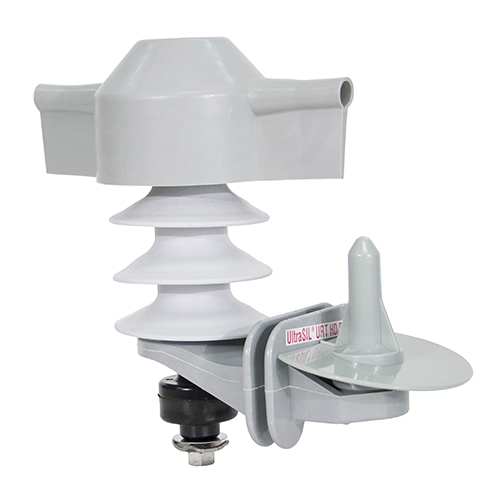
A downlead clamp is a mechanical device for attaching vertical or downward-running cables to poles, structures, or equipment frames. The clamps can secure and protect cables from movement, friction, and environmental damage. Downlead clamps are commonly employed in electrical transmission systems, control panels, grounding installations, and equipment for processing high-voltage battery cells. They provide cable support, improve fire prevention, and shield electrical lines from Peru’s varied climatic conditions. The following are the functions of downlead clamps in the building of a lithium battery facility in Peru.

- Cable management and stability—downlead clamps prevent cables from swinging, ensure neat, organized routing, and reduce the risk of short circuits. They are crucial during cell assembly or recycling.
- Electrical grounding support—downlead clamps work alongside earthing systems that are vital for discharging stray electrical currents, preventing electrocution and equipment damage. The clamps help in keeping grounding conductors in place.
- Fire prevention and hazard control—battery processing involves flammable materials and heat-sensitive systems. Downlead clamps prevent cable insulation from wearing due to friction or heat. They also reduce the chance of cable faults or arcs, which can cause fires.
- Support for automation and monitoring systems—modern battery plants use industrial IoT sensors, cameras, and robotic arms. These components use downlead clamps to help manage sensor and control system wiring. They also ensure signal integrity by preventing cable twisting or breakage.
- Environmental protection—downlead clamps are from corrosion-resistant materials that ensure resistance to UV radiation, rain, and chemical exposure. They also ensure fewer maintenance issues in remote or rugged plant locations.
Key obstacles for the development of lithium battery factories in Peru
Peru’s mineral riches and geographical location give it the potential to become a major role in the global lithium battery supply chain. Despite rising global demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems, Peru has yet to leverage on this opportunity. The use of downlead clamps helps to prevent equipment failures, improve safety compliance, and streamline plant maintenance. It faces some hurdles and structural constraints, including

- Limited industrial infrastructure—Peru lacks existing industrial infrastructure to support large-scale battery production. Limitations include insufficient industrial-grade energy supply, underdeveloped transport and logistics networks, and limited access to advanced machinery and automation equipment.
- Underutilized lithium reserves—commercial extraction has not commenced due to legal and environmental approvals and conflicts with indigenous communities. Battery plants would rely on imports that increase operational costs and limit vertical integration.
- Energy security and sustainability—battery production is energy-intensive, and we aim for energy reliability. Power interruptions can damage sensitive battery production processes and reduce efficiency.
- Environmental and social concerns—lithium battery production and recycling involve high water usage, potential chemical leaks, and risk of air and soil contamination. Also, strong opposition from communities may lead to project cancellations.